
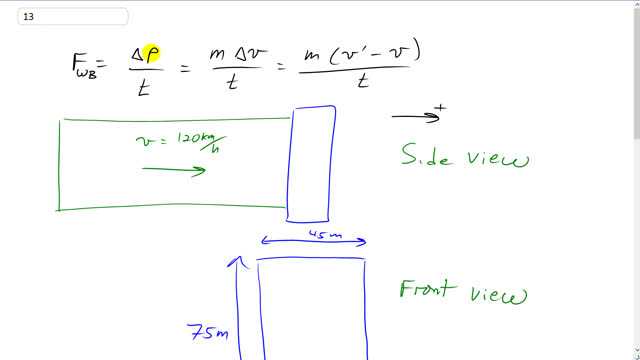
Air in a 120-km/h wind strikes head-on the face of a building 45 m wide by 75 m high and is brought to rest. If air has a mass of 1.3 kg per cubic meter, determine the average force of the wind on the building.
In order to watch this solution you need to have a subscription.
This is Giancoli Answers with Mr. Dychko. We can find the force on the wind due to the building that it collides with by finding the rate of change in momentum of the wind. So the change in momentum is gonna be the mass of the air column here that collides with the building multiplied by its change in velocity divided by the time over which this change in velocity occurs. So we are told that the wind is going at 120 kilometers an hour so let's take our time to be one hour; and what mass of air is gonna be colliding with the building in an hour, that's what the m represents. Well, we'll take the density of air and multiply it by the volume of this column; it has a length of 120 kilometers or 120 times 10 to the 3 meters after an hour and it has a cross section, here's a front view of the building of 45 meters across and 75 meters high so in an hour, the total mass of air to hit the building will be the column volume which is 45 meters multiplied by 75 meters times 120 times 10 to the 3 meters all multiplied by—the density of air— 1.3 kilograms per cubic meter and that gives 5.265 times 10 to the 8 kilograms of air. And then the force on the wind due to the building is gonna be this mass that we just calculated times wind's final velocity of zero because it gets stopped by the building and we are told that it doesn't bounce back so the wind stops and so it's final velocity is zero after collision and minus the 120 kilometers per hour expressed in meters per second multiplied by a 1000 meters for every kilometer and then multiply by 1 hour for every 3600 seconds and divide that by an hour expressed in seconds and you get negative 4.9 times 10 to the 6 newtons and the force on the building due to the wind which is what we are told to find is the Newton's third law counterpart to the force on the wind due to the building and these are gonna be equal and opposite and so we have negative of negative 4.9 times 10 to the 6 and we end up with 4.9 times 10 to the 6 newtons is the force on the building due to the wind.