
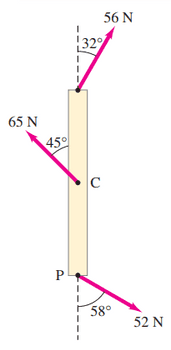
Determine the net torque on the 2.0-m-long uniform beam shown in Fig. 8–45. All forces are shown. Calculate about
- point C, the CM, and
- point P at one end.
In order to watch this solution you need to have a subscription.
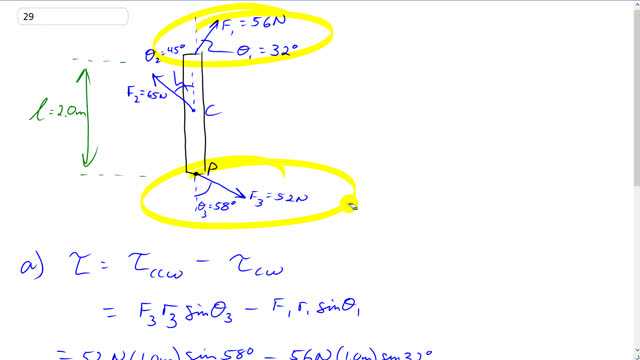
This is Giancoli Answers with Mr. Dychko. So for part (a) when we are calculating the torque about this center point C, only the F 1 at the top and F 3 at the bottom have any lever arm so they are the only ones that result in any torque. This force here is... there's no distance between the point where it's applied and the pivot point and so there's no lever arm so there's no torque resulting from F 2. So the lever arm for both forces 1 and 3 is 1 meter—half the length of the beam— and so we'll take the total torque is gonna be the total counter-clockwise torque minus the total clockwise torque. F 3 is exerting a counter-clockwise torque so we take F 3 multiplied by r 3, which is 1 meter, times by sin of Θ 3, which is 58 degrees, and then minus F 1, 56 newtons, times its lever arm, 1 meter, times sin of 32 degrees and we get 14 newton meters is the total torque above the center of the beam and being positive that means it's counter-clockwise. And for part (b), we are asked to calculate the net torque about the point P at the bottom of this beam that means F 3 now exerts no torque whereas F 1 and F 2 both have a torque. And the lever arms are gonna be 2 meters for F 1 because this point here where F 1 is applied is 2 meters away from the pivot point and for F 2, the lever arm will be 1 meter. So we have the total torque is 65 newtons times 1 meter times sin 45 that's the torque due to this force here and then that's gonna be counter-clockwise; and then clockwise, we have 56 newtons times 2 meters times sin 32 for a total of negative 13 newton meters the negative sign means the total torque is clockwise.
In part A I can you explain how you arrived at 14 Nm? I keep getting 20.75
Hello reidy,
Thank you for the question. I wish I'd gotten back to you sooner. The answer of 20.75 is what your calculator will tell you if it is in radian mode. Since the angles here are in degrees, your calculator needs to be in degree mode. How to switch will depend on your model of calculator, but you can always check the mode by entering and it will tell you "0.5" if it's in degree mode. There will usually be a rad displayed somewhere when it's in radian mode.
All the best,
Shaun
How is force 2 of 65N counter clockwise? I must be visualizing it differently. I see clockwise. Can you perhaps give an insight into how I can see this?
Hi acw, I would imagine a nail stuck through the point P at the bottom of the beam in order to fix that end as the pivot (for part (b)). Force 2 in that case would move the top of the beam to the left, and the beam is like a clock hand going in the opposite direction to a clock (counterclockwise, in other words).
All the best,
Shaun