
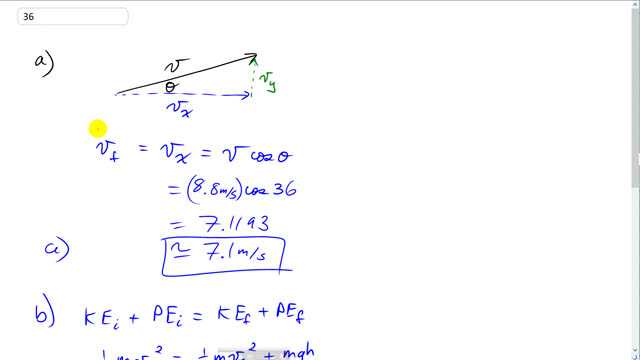
A 0.48-kg ball is thrown with a speed of 8.8 m/s at an upward angle of .
- What is its speed at its highest point, and
- how high does it go? (Use conservation of energy.)
In order to watch this solution you need to have a subscription.
This is Giancoli Answers with Mr. Dychko. This ball is initially thrown at an angle of 36 degrees and with a speed of 8.8 meters per second; and we have to find out what the velocity will be when it's at the highest point. And at the highest point, it's going to go just horizontally; the vertical component of its velocity will be zero. And so the final velocity will be the x-component of its initial velocity which is not going to change, at all, during its travels, along this parabola. And so we have, 8.8 meters per second times cos 36; cos because it's the adjacent leg of this vector triangle and we get 7.1 meters per second is the x-component of its velocity, which will be its final velocity at the top of its ark. For part (b), we have to use conservation of energy to figure out the maximum height. So we know the initial kinetic plus potential equals the final kinetic plus potential. And, initially, there's no potential energy because we'll take the reference level to be the level that, at which, it's initially thrown. So it has just kinetic energy to begin with; one-half m v initial squared and that equals one-half m v final squared, at the maximum height, plus the gravitational potential up there. So the m's cancel everywhere, and we can move this term to the left side so it becomes v initial over 2 minus v final over 2. And then divide both sides by g. And then we have, h is, after you switch the sides around, the initial squared minus v final squared over 2g. So that's 8.8 meters per second squared minus the answer for part (a), squared, and then divide by 2 and divide by 9.8 and you get 1.4 meters is the maximum height it will reach.
what about the 1/2's? don't they cancel?
Hi maizer01, thanks for the question. Are you referring to the 1/2 in front of each kinetic energy term in part b)? They don't cancel since 1/2 is not a common factor of all terms. There is a potential energy term which is not multiplied by 1/2, which means 1/2 is not a common factor.
All the best,
Mr. Dychko