The rms speed of molecules in a gas at is to be increased by 4.0%. To what temperature must it be raised?
In order to watch this solution you need to have a subscription.
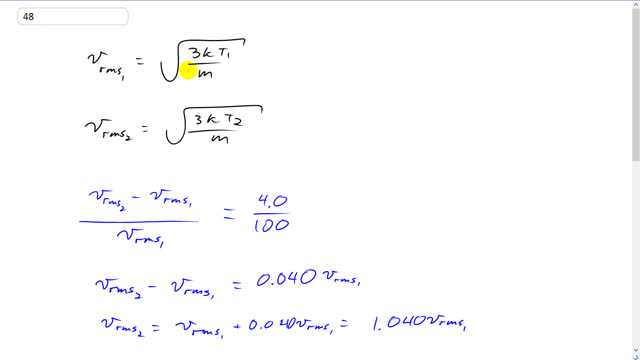
This is Giancoli Answers with Mr. Dychko. We're going to raise the rms speed of a molecule by 4% and the first rms speed that it'll have is going to be square root of 3 times Boltzmann's constant times the first temperature divided by mass. And the second rms speed is going to be square root of 3 K T2, second temperature divided by the same mass cause it's the same molecule, the only thing we're changing is the temperature. So, it increases speed by 4% means that the difference in speeds in the second case versus the first case divided by the first speed is going to be 4% or 4 divided by 100. And we can multiply both sides by V rms1 and that means V rms2 minus V rms1 is 4% times V rms1. 4.0 dividede by 100 is 0.040. And then take this term to the right hand side. And you get V rms2 equals V rms1 plus 0.04 V rms1 which is 1.04 V rms1. So, let's substitute into this line, on the next line. V rms2 is square root 3 K T2 over m. And that equals 1.044 times square root of 3 K T1 over m. The... You can multiply both sides by square root m over 3 K to cancel a bunch of things. And that leaves us with square root T2 equals 1.04 times square root T1. So, the temperature in the second case to increase the rms speed by 4% is going to be 1.04 squared times T1 1.04 squared times the temperature in kelvin, 20 degrees Celsius plus 273.15, which gives 317 kelvin. And we take away 273.15 to find the temperature in degrees Celsius of 43.9.
