Determine the time it takes for a satellite to orbit the Earth in a circular near-Earth orbit. A “near-Earth” orbit is at a height above the surface of the Earth that is very small compared to the radius of the Earth. [Hint: You may take the acceleration due to gravity as essentially the same as that on the surface.] Does your result depend on the mass of the satellite?
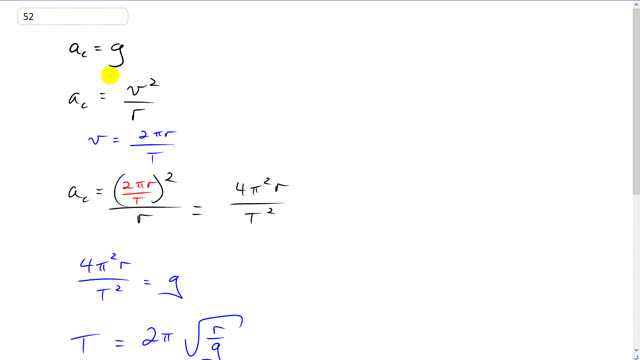
In order to watch this solution you need to have a subscription.
This is Giancoli Answers with Mr. Dychko. Since we have a near-Earth orbit, we can say that the centripetal acceleration of the satellite will be the same as the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the Earth because it's pretty close to the surface. Now, centripetal acceleration is also v squared over r and we are gonna rewrite this, in terms of period, so that we can figure out how long it takes for this one orbit to happen. So, we'll rewrite v as 2πr over T; 2πr is the circumference of the satellite's circular path and then divided by T is the period; the total time it takes to travel that full circle. So we substitute that in for v, in this formula here. And I have written that in red, the substitution. So, we have 2πr over period, all squared, divided by r and that's the centripetal acceleration. And so that becomes 4 π squared and it's r to the power of 1 because it's r squared divided by r makes r to the 1, all over T squared. And then, we'll set this equal to g, and that's in the next line here, and we'll solve for T. So I multiply both sides by T squared and divided both sides by g and end up with T squared equals all 4 π squared r over g. And then take the square root of both sides and you can take the 4 π squared out of the square root and turn it into 2π by square rooting them. So T is 2π times square root r over g. So that's 2π times the square root of 6.38 times 10 to the 6 meters— radius of the Earth— because it's in near-Earth orbit so the orbital distance from the center of the Earth is, pretty much, the radius of the Earth divided by 9.8 meters per second squared and that gives 5069.6 seconds and times by 1 minute for every 60 seconds will give us a number, that we can relate to bit better, 84.5 minutes. So, let's just put an hour and a half or so to do one complete orbit.
