
If a compressive force of is exerted on the end of a 22-cm-long bone of cross-sectional area ,
- will the bone break, and
- if not, by how much does it shorten?
- the bone will not break
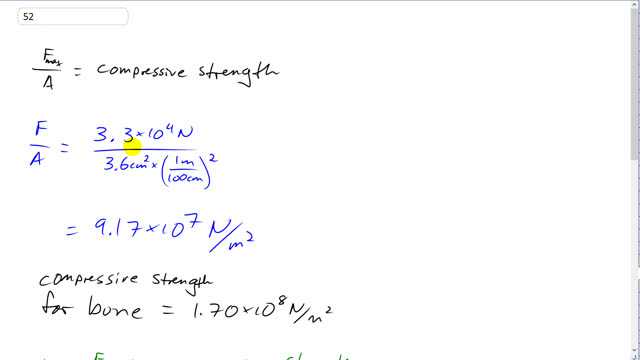
In order to watch this solution you need to have a subscription.
This is Giancoli Answers with Mr. Dychko. The maximum stress that a bone can tolerate equals its compressive strength and the force that's actually being applied to this bone is 3.3 times 10 to the 4 newtons and we divide that by its cross-sectional area of 3.6 centimeters squared converted into meters squared by multiplying by 1 meter for every 100 centimeters squared and that gives 9.17 times 10 to the 7 newtons per square meter. Now since that stress is less than the compressive strength of bone, which is 1.70 times 10 to the 8 newtons per square meter, that means the bone will not break because this is the maximum stress it can tolerate and this is the stress that it's experiencing. So it has another order of magnitude it can go still before it breaks. And the amount that it shrinks... well, we can rearrange this formula to say that the stress equals the elastic modulus times the change in length divided by its original length and we'll solve for Δl by multiplying both sides by l naught over elastic modulus and then switch the sides around and we get Δl is original length times the force applied to compress the bone divided by its elastic modulus times its cross-sectional area. So that's 22 times 10 to the minus 2 meters— original length— converting centimeters into meters there with the 10 to the minus 2 times 3.3 times 10 to the 4 newtons divided by 15 times 10 to the 9 newtons per square meter—elastic modulus of bone— times 3.6, you know, centimeters squared converted into meters squared and that gives 0.00134 meters and we can write that as 1.3 millimeters.